Have you ever thought about how apps like TikTok, Uber, or Instagram, with simple ideas, grew into billion-dollar businesses?
Each of these apps started with the aim of solving a common problem that millions of people face.
But turning an idea into a global success takes more than just inspiration. It requires a clear, well-planned app development process. Which is where a professional mobile app development company can make all the difference.
The process of mobile app development has shifted from primarily coding. Now, it is about growable and risk-free applications, developing for the user, and combining modern technologies, like the cloud, APIs, and AI, to provide uninterrupted experiences across iOS and Android.
For startups, apps are a way to validate ideas and attract users. For enterprises, they’re tools to boost engagement and efficiency. Mobile applications are revolutionizing industries globally. In simple words, mobile apps are a crucial part of the global digital economy.
According to Statista, by the year 2027, the total spending of both the Google Play Store and App Store will collectively reach 186 billion U.S. dollars. It will reflect an increase of 50% compared to the year 2024.
With all of the fast growth and development in mobile apps, knowing the mobile application development process step by step can be the difference between an app that fails and one that succeeds.
In this blog, we will share everything you need to know about building a successful app from ideation to launch and beyond.
CTA SECTION START
cta title: Turn your app idea into reality with Inceptives Digital. Get in touch us today.
cta des:
cta button: Talk to an Expert
CTA SECTION END
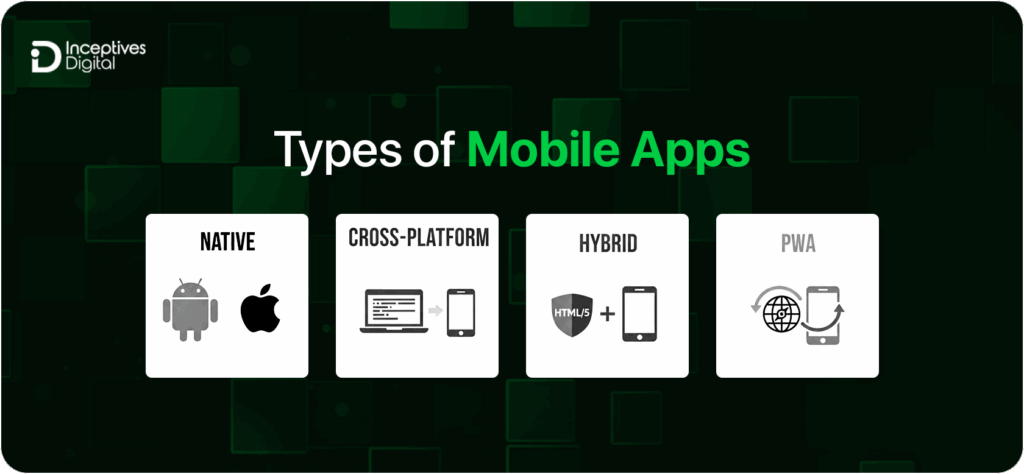
Types of Mobile Apps
If you are thinking of building an application for your business, you should consider these key factors before choosing the type of application:
- Budget
- Target audience
- Performance needs
- Time to market
- Long-term goals
Below are the types of applications discussed in detail to help you decide which will be the right choice for you.
Native Apps
Native applications are platform-specific, for example, Swift for iOS and Kotlin for Android. Native apps are best considered for performance and device hardware integration. However, native app development is costlier and more time-consuming because you need to develop different versions for each iOS and Android platform.
Cross-Platform Apps
Cross-platform applications are capable of running on both iOS and Android platforms with a single codebase powered by technologies like Flutter, React Native, or Xamarin. If you want to reduce development cost and time, you should definitely consider this type.
Hybrid Apps
Hybrid applications merge web technologies such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript with features of native apps, so they can run on multiple platforms at the same time. If you want to develop faster and access device features (camera, GPS, notifications) without developing completely in native, hybrid applications are a good option.
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs)
PWAs are browser-based applications but provide offline access like native apps, push notifications, and home screen installation. They are easy to maintain but lack hardware integrations.
When to Choose Which Type:
| App Type | Best When You Need | Avoid If… |
| Native Apps (Swift, Kotlin) | Maximum performance, security, and advanced features (e.g., banking, gaming, AR apps) | Budget and timeline are limited, or you need both iOS & Android quickly |
| Cross-Platform Apps (Flutter, React Native, Xamarin) | Faster launches on both iOS & Android with a single codebase | You require highly complex, platform-specific features |
| Hybrid Apps | Quick, budget-friendly solution for simpler apps or MVPs | You want high performance and advanced UI/UX |
| Progressive Web Apps (PWA) | Wide accessibility, lightweight apps, easy updates without app store approvals | You need full device integration (camera, GPS, sensors) or complex offline functionality |
CTA SECTION START
cta title: Not sure which app type is right for your business?
cta des:
cta button: Let’s Discuss Now!
CTA SECTION END
Step-By-Step Mobile App Development Process
Delivering a mobile app project isn’t just about writing code. You need to have an overall plan and structure for your development process to make sure that the app performs, is secure, and offers a great user experience. Below, we have identified the full mobile app development process and provided steps to take you through the process:
Ideation & Research
There are millions of applications on the Play Store and App Store collectively, but how many do you know by name? There will definitely be a few of them. The reason behind most of the applications failing is poor planning and research. For example, a research study revealed that 90% of mobile apps fail within the first year after launch, generally due to insufficient market research or poor implementation. Below are the significant steps you are going to follow.
| Step | Description |
| 1. Problem Identification | Clarify the problem your app is gonna solve and how it is relevant to the users. |
| 2. Market Research | Examine current market trends, what’s in demand, and evaluate your idea. |
| 3. Competitor Analysis | Study your potential competitors to find market gaps, weaknesses, and strengths. |
| 4. User Persona Development | Do potential users’ profiling in terms of demographics, requirements, and behaviours. |
| 5. Value Proposition | Identify your app’s USP and why users should prefer it over competitors. |
| 6. Feature Brainstorming | Generate and prioritize feature ideas aligned with user and business needs. |
| 7. Feasibility Study | Evaluate the technical, financial, and operational viability of the concept. |
Planning & Strategy
After finalizing your idea, it’s time to develop a strategy or a clear roadmap to avoid any delays and risks. Here is how to do that:
| Step | Description |
| 1. Define Objectives | Clearly articulate the purpose of the app, metrics for success (e.g. downloads, engagement, revenues), and anticipated deliverables (i.e. milestones). |
| 2. Feature Roadmap | Categorizes features based on user-derived priorities and business objectives. |
| 3. Technology Stack Selection | Choose the right programming language, frameworks, and tools that will allow flexibility to scale and future maintenance. |
| 4. Resource Allocation | Decide who takes on designer, developer, tester, and project manager roles. |
| 5. Budget Planning | Estimate budget for design, development, testing, launch, and maintenance. |
| 6. Timeline & Milestones | Draft timeline for schedule development with achievable sprints or delivery phases. |
| 7. Risk Assessment | Consider possible risks (technical, financial, or market)? Consider mitigations. |
Design UI/UX

A user interface is the first thing visitors will encounter. And it is a fact that the first impression is the last impression. So a UI/UX can make or break your app’s success. A study found that a good user interface can increase the conversion rate of a website up to 200%. Here is how you can achieve those numbers.
| Step | Description |
| 1. Requirement Gathering | Capture user requirements, business goals, and functional requirements through research in order to set the direction for the design. |
| 2. Wireframing | Make low-fidelity wireframes that demonstrate the app organization and navigation at the screen level. |
| 3. Prototyping | Build a clickable prototype to visualize the user flow, navigation, and experience. |
| 4. High-Fidelity Design | Design pixel-perfect UI screens in the final design tool for delivery, such as Figma, Adobe XD, or Sketch. |
| 5. Accessibility Compliance | Follow the WCAG guidelines to ensure the design can be usable for everyone, including those with a disability. |
| 6. Usability Testing | Conduct usability testing to get evidence from actual users on navigation, layout, and experience. |
| 7. Iteration | Use feedback from the usability testing to iterate on the designs before moving into development. |
Frontend and Backend Development

Once the design is ready, it is now time to bring this design to life by adding functionality and interactivity to your design. To do that, you have to develop a code base for it. Adding a code base means giving it a brain to function and interact. The app development has two phases:
- Frontend (for visual aspects)
- Backend (for site structure, data, and logic)
Here are all the details about app development phases:
| Aspect | Frontend Development | Backend Development |
| Definition | The client-side of the app that the user interacts with (UI & UX). | The server-side of the application. It handles data, logic, and integrations. |
| Main Role | The visual design, navigation, and interactive components of an app are designed to provide the user with a seamless experience. | The technology that allows an application to function. It handles how the application communicates with databases, APIs, authentication, and the server logic. |
| Technologies & Languages | Swift (iOS), Kotlin (Android), JavaScript, Dart (Flutter), React Native. | Node.js, Python, Java, PHP, Ruby, .NET, Firebase, AWS Lambda. |
| Key Components | Layouts, buttons, animations, gestures, typography, and responsiveness. | Databases (MySQL, MongoDB, PostgreSQL), APIs, cloud servers, and authentication systems. |
| User Interaction | Directly interacts with the end user (taps, swipes, inputs). | Works in the background to process user requests and send data to the frontend. |
| Performance Factors | All performance factors, including app responsiveness to the user request, overall load times, and the smoothness of element visuals. | Determines scalability, speed of data processing, and security. |
| Testing Focus | UI & UX testing, compatibility across devices, responsiveness, and accessibility (WCAG testing if required). | Security testing, API validation, database performance, and server load handling. |
| Dependencies | Dependent on the backend for data and business logic. | Relies on the frontend to display and interact with processed data. |
Testing & QA

Quality assurance is more than just bug finding. It is a systematic approach to everything that can assess functionality, performance, security, and cross-platform consistency both before and after a release. An app that is poorly tested is at risk of high uninstall rates, issues driving compliance, and loss of consumer trust. According to Zipdo, 38% of users abandon an app after just one use due to crashes or bugs. You can get away with this issue by following the steps:
Core testing practices include:
- Functional Testing: It verifies the functioning of features against specifications and business logic.
- Performance Testing: It determines how many users load, response times, and resource usage under load.
- Compatibility Testing: It tests the application on iOS, Android, device types, screen resolutions, and OS versions.
- Usability Testing: Confirms intuitive navigation, accessibility compliance (WCAG), and user experience standards.
- Security Testing: It simulates attacks to find vulnerabilities, reveals issues with encryption, and potential data leaks.
Tools Used:
- Appium
- Selenium
- Espresso
- XCUITest
Deployment & Launch

After passing the QA your application is ready to deploy and launch on app stores. You have to follow the Google Play Store and the Apple App Store guidelines, which include app security, design standards, data privacy, and performance requirements. The developers will create signed build files (APK for Android, IPA for iOS) and properly configure backend servers, APIs, and cloud hosting for the backend functionality of the application to be connected and operational.
Key steps include:
- App Store Compliance: Fulfilling rigid review standards from Apple and dealing with policy requirements from Google so that your app isn’t rejected or flagged for ethical violations.
- Release Management: Setting up signed binaries, app bundles, and provisioning profiles.
- App Store Optimization (ASO): Optimizing your titles, descriptions, keywords, and screenshots for discoverability.
- Phased Rollout: Using a staged rollout (via TestFlight or Google Play Console) and beta testing to get a sense of the app’s stability before full launch.
- Monitoring Tools: Setting up analytics (like Firebase, App Center) and crash reporting (like Sentry, Crashlytics) to monitor initial performance.
An app launch is more than just pushing a ‘Publish’ button. The expected stability, compliance requirements, and discoverability of your app are all important aspects to maximize adoption from day one.
Post Launch Activity
Choose trusted mobile app developers to make sure your app runs smoothly even after the launch. The app’s launch is just the start of the process. Ongoing monitoring, revision, and improvement of app performance and functionality provide long-term app success.
Key activities typically include:
Bug Fixes & Patching: Fixing new errors and crashes reported by users rapidly preserves app stability.
Regular Updates: Regularly adding features, improvements to the user interface and user experience design, and enhancements to security preserve the value of the app in the marketplace.
Scalability Planning: Scalability planning helps to ensure proper functioning for existing and new users. For consideration is developing a business plan and user growth plans to alter the back-end APIs, databases, and infrastructure to provide growing user traffic while considering downtime.
User Feedback Integration: Regular collection of reviews and ratings, in-app analytics (for example, Mixpanel, Firebase Analytics) for improved usability in terms of use by end-users.
Security issues: Apply updates for regulatory compliance (for example, new GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS updates were optioned). Patch all security-related vulnerabilities for data protection.
Performance Monitoring: Use Application Performance Monitoring (APM) tools (for example, New Relic, AppDynamics) to navigate load times and crashes, and overall responsiveness.
A well-planned post-launch strategy will help to ensure that your mobile app isn’t just surviving in an increasingly competitive market, but thrives because it provides end-user value in terms of consistent performance, user satisfaction, and business growth.
CTA SECTION START
cta title: We follow this proven process to deliver apps that succeed.
cta des:
cta button: Let’s build yours today
CTA SECTION END
Technology Stack for Mobile App Development

Choosing the appropriate technology stack is critical in mobile app development. Your stack will determine the performance, scalability, and long-term sustainability of your app.
Frontend Technologies
Native applications leverage Swift (iOS) and Kotlin (Android) for speed and reliability. For cross-platform applications, React Native and Flutter allow for faster delivery with “near-native” performance.
Backend Technologies
Backend technology enables applications, business logic, APIs, and integrations. Node.js is a common choice for real-time applications. Django and Ruby on Rails enable secure and rapid development. Many enterprises choose .NET for larger applications. GraphQL can also improve API efficiency and reduce the data load.
Databases
If your data is structured, MySQL or PostgreSQL is likely best for your app. If your data is unstructured, start with MongoDB. If you’re building chat or collaboration apps, your data probably needs to be updated immediately, so the Firebase Realtime Database will be a great choice.
Cloud Platforms
AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud deliver scalable hosting, AI services, and global reach.
DevOps & CI/CD
To manage your builds, testing, and deployments, use a tool like Docker, Jenkins, or Kubernetes. Your development team will have safer, faster releases!
In short, choose the right technology stack to set a strong foundation for your mobile app development. The technology stack will influence the performance, scale, and evolution of your mobile app and its ability to adapt over time. Here is a table that lists the technology stack by app types:
Technology Stack by App Type
| App Type | Frontend | Backend | Database | Cloud / DevOps | Best For |
| Native iOS | Swift | Node.js / Django / .NET | MySQL / PostgreSQL | AWS / Azure + Docker, Jenkins | High-performance iOS apps with rich UI/UX |
| Native Android | Kotlin | Node.js / Ruby on Rails / .NET | PostgreSQL / MongoDB | Google Cloud + Kubernetes | Feature-rich Android apps with deep OS integration |
| Cross-Platform | React Native (JavaScript) / Flutter (Dart) | Node.js / Django | MongoDB / Firebase | AWS / Google Cloud + Jenkins | Cost-effective apps running on both iOS & Android |
| Hybrid Apps | HTML5, CSS, JavaScript (Ionic, Cordova) | Node.js / Django | MongoDB / Firebase | AWS + Docker | Simple apps with faster market entry |
| Progressive Web Apps (PWA) | Angular / React.js / Vue.js | Node.js | Firebase / MongoDB | Google Cloud | Lightweight, browser-based mobile experiences |
Monetization Strategies for Mobile Apps

A smart monetization strategy is the key to making an application profitable. Do you know? According to a research study, the revenue share of subscription-based apps is 44% of the total global app revenue. You too can generate a high revenue from your app with the right approach, according to your specific requirements.
Freemium Model
In the freemium model, the basic features are available to users without a fee, but to access advanced and premium features, the user has to buy a plan. SaaS and productivity apps mostly use this model.
In-App Purchases (IAPs)
Applications like gaming and lifestyle use the In-app purchases model. The revenue is directly generated by selling in-app products like coins, skins, and premium features.
Subscription Model
Recurring payments could be monthly or yearly, and all payment models provide predictable revenue. Media apps like Spotify and Netflix rely primarily on this model. A great way to maximize retention is with tiered plans in case users want to upgrade (basic, premium, enterprise).
In-App Advertising
The use of ads, banners, interstitials, videos, or native ads can help a free application earn without upfront payments from the user. This is a scaling method, but would warrant some consideration on the low-rate ends of these because at high frequencies, the ads devalue the user experience.. For example, leveraging platforms like Google AdMob will allow you to run highly-targeted chargeable campaigns as revenue grows.
Paid (One-Time Purchase)
Users pay a one-time download fee once and can access the features of the app. This model is typically best for niche or utility apps that limit ongoing costs.
Affiliate & Partnership Marketing
Apps that promote the partner’s products/services directly within the app and earn a commission when users convert are especially successful in the finance, travel, and e-commerce app areas.
Hybrid Model
Many apps are likely to apply some combination of strategies, for example, free download ads + optional subscriptions, combined to improve multiple revenue streams in an app.
Common Challenges in Mobile App Development & How to Overcome Them

Developing a mobile application entails more than pursuing a software coding exercise. It is about tackling technical, regulatory, and marketing challenges. Below are some hurdles encountered most commonly in the app development process, along with tested solutions to overcome them:
Security & Data Privacy
Mobile apps generally handle sensitive user data, which makes them juicy targets for cyber crooks.
Solution: End-to-end encryption, compliance with GDPR/CCPA, making sure the APIs are secure, and remediating any vulnerabilities on a timely basis. Operate penetration testing for every release cycle.
App Store Rejection
App Store and Google Play Store maintain strict guidelines concerning everything, from UI/UX guidelines to data policy.
Solution: Before even formatting your app for submission, you must read App Store Review Guidelines and Google Play Policies to understand and check that your metadata is correct. Finally, stage your app in real world beta testing on TestFlight or through Play Console.
Device Fragmentation
Device fragmentation often compromises app performance when there are maximum possible device display sizes, the most distinct OS versions in history, and the level of hardware configurations. These items quickly determine how an application behaves and experiences.
Solution: Consistency across platforms would also mean testing an app with responsive design, various devices, and emulators, supplemented by cross-platform frameworks like Flutter or React Native.
Scalability
An application might work perfectly for a thousand users, but it will probably not work well for a million unless it has been built for scalability purposes.
Solution: Use a cloud platform (AWS, Google Cloud, Azure) and implement load balancing and a microservice architecture for scalability.
High Competition
Hundreds of thousands of applications make it a troublesome phase where discoverability and retention become issues.
Solution: Apply App Store Optimization (ASO), run user-centric paid ads, and use user-centered design with continuous feedback to improve retention.
Your Shortcut to Successful App Development
Mobile app development is not just a coding task. It is a comprehensive process that encompasses planning, design, testing, and ensuring the results meet your expectations. Managing all these tasks single-handedly can be hectic, and getting stuck somewhere is very likely. For businesses looking to expand across America, we recommend hiring a trusted mobile app development company USA with a proven portfolio.
Inceptives Digital is a mobile app development agency with 8+ years of industry experience. Imagine us as your development partner who will be there for you at every stage of the development lifecycle. We have delivered 70+ projects in 20+ industries. We develop applications that are not only fast and reliable but visually appealing as well. We would love to help you develop an application that drives results.
So, if your idea is ready to blossom into an application, let’s make it happen together.
CTA SECTION START
cta title: Turn Your Idea Into Reality With Inceptives Digital
cta des:
cta button: Let’s Start Your Project!
CTA SECTION END
Mobile App Development FAQs
Below are the 7 stages of mobile app development:
Ideation and Research
Planning and Strategy
UI/UX Designing
Development
QA and Testing
Deployment and Launch
Maintenance
The main types of app testing include:
Functional
Usability
Performance
Security
Compatibility testing
AI will not replace mobile development but rather change it. AI tools can help be more efficient in coding, testing, and design recommendations. But to create a successful app, human creativity, strategy, and understanding of user needs are required, which AI will not equally possess. So, we do not see AI replacing developers. We see AI supporting developers in their productivity to enhance their overall output and innovation in mobile app development.
In short, yes. The global mobile app development market is estimated at approximately $585.68 billion in 2025.
AI enhances mobile app development by automating wireframing, coding, and testing. It enables features like chatbots and fraud detection. While not replacing developers, AI speeds up the process, cuts costs, and aids in creating smarter, personalized apps.
SIDEBAR LIST START
- What is Mobile App Development? A Beginner’s Guide
- Types of Mobile Apps
- Step-By-Step Mobile App Development Process
- Technology Stack for Mobile App Development
- Monetization Strategies for Mobile Apps
- Common Challenges in Mobile App Development & How to Overcome Them
- Your Shortcut to Successful App Development
- Mobile App Development FAQs
- Conclusion
SIDEBAR LIST END